June 4th, 2015 § § permalink
Follow me on Twitter. Seriously.
It’s been a little over five years. I wrote my first post on this blog, The Mysteries of Funny Looking Sperm, April 18, 2010. At the time, this blog was very much an experiment, and I had no idea how it would work. In my daily life, I see a lot of men with difficulties having children or other male health problems, and they don’t tell you anything about that when you take “sex ed” in high school. Lots of men share the same problems, and I would say the same things to different men throughout the day. So I thought that I would put my end of those conversations in a general way on a blog, so that men around the world with questions about male reproductive health might find some answers.
My first few blog posts came from those common conversations. I see a lot of men with male endocrine problems, so I wrote a few posts on how the endocrine system works in a man and how it can be fixed if needed. I wrote about concerns like, can a man’s underwear cause problems with his sperm? At first, I shut off comments after two weeks, but I quickly realized that many people found my posts not by reading the blog start to finish, but through a search for a specific concern. That makes a lot of sense: I do that, too. People would be coming at a post weeks, months, or even years after I wrote it. My third post on April 28th, 2010, How Clomid Works in Men, is still my most visited one with 874 comments as of today.
After a while, people started asking great questions in the comments. Sometimes I could answer them in a couple of lines in the comments section, but some required longer answers. I added posts for a few of these great questions. Understandably, although I tried to make it very prominent in the FAQ, people would still ask me medical questions about themselves and their loved ones. It’s really frustrating, but I can’t answer them. I don’t have the basic information through the web that all doctors need to make a diagnosis and treat a patient, which includes a physical examination. I need to see people in person to be their doctor.
As the blog evolved, I began posting about news events, important scientific studies, and general items of interest in male health. But most people still come across the blog by searching for a specific problem or question, and that’s the way it mainly seems to work. So for those who read a post from years past and have a question, I’ll often recommend reading the comments and other posts on the blog, as the answers are usually there.
But if you’re interested in male health, and you want a more up-to-date stream of information, then follow me on Twitter. I post pretty frequently there, often with links to important news articles about male health and the other parts of my job in science, engineering, and education. You’ll even see my human side from time to time. I’ll of course still write here on this blog when the need for more words arises.
See you in the Twitterverse!
March 13th, 2013 § § permalink
As I’ve written before in this blog, clomiphene is an effective if off-label treatment for men with low testosterone who want to preserve their fertility. If used directly, testosterone itself actually decreases the making of testosterone and sperm in a man’s testis. Clomiphene increases testosterone production in the testis by increasing the pituitary hormones that tell the testis to make testosterone.
In the March issue of Fertility and Sterility, a journal that I co-edit with Dr. Antonio Pellicer, Drs. Kim and co-authors review the published medical literature on treating low testosterone with clomiphene and other drugs besides testosterone. They conclude that clomiphene is a safe and effective treatment for men with low testosterone and note that less than one year of treatment with testosterone is usually reversible if a man wants his fertility to return. Unfortunately, we don’t know all that much about longer treatments with testosterone, and many men who have been on testosterone for several years do not have sperm return even with other forms of treatment.
Drs Kim and co-authors give us a nice review that supports the use of clomiphene for men with low testosterone who want to preserve their fertility.
April 28th, 2010 § § permalink
With the suspension of Cincinnati Reds pitcher Edinson Volquez for performance enhancing drug use and a swirl of rumors that the agent involved was clomiphene (also known as Clomid,) I thought it timely to write about how clomiphene works and how it’s used. From what I read on the internets, there is an enormous amount of misinformation floating around out there.
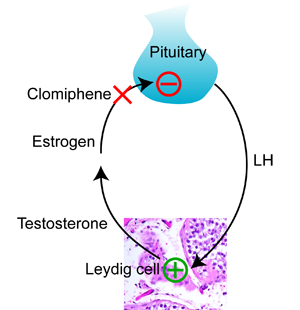
To understand how clomiphene works, you need to know how the pituitary controls the making of testosterone in the testis. Testosterone is made by Leydig cells in the testis, which I explained in my last post. The pituitary releases a hormone called luteinizing hormone (“LH”) that stimulates the Leydig cells to make testosterone. Testosterone is converted to the female hormone estrogen, (which I also explained in my last post,) and estrogen tells the pituitary to stop making more LH. This kind of negative feedback system is common when it comes to how hormones work. It’s just like a thermostat and heater. As the room gets warmer, the thermostat sends less electricity to the heater. When the room gets colder, the thermostat sends more electricity to the heater.
Clomiphene works by blocking estrogen at the pituitary. The pituitary sees less estrogen, and makes more LH. More LH means that the Leydig cells in the testis make more testosterone.
As I explained in my last post, giving testosterone to a man does just the opposite. The pituitary thinks that the testis is making plenty of testosterone, and LH falls. As a result, the testis stops making testosterone, and the usually high levels of testosterone in the testis fall to the lower level in the blood.
So clomiphene is a way to increase testosterone in the blood and the testis at the same time. It preserves testis size and function while increasing blood testosterone.
Unfortunately, clomiphene is not FDA approved for use in the male. Like most of the medications that we use to treat male fertility, the pharmaceutical company that originally sought approval by the FDA did it for women. Clomiphene is now generic, and it’s unlikely that anyone will pony up the hundreds of millions of dollars necessary to get it approved for the male. That’s the bad news. The good news is that it means that this medication is fairly inexpensive, cheaper than most forms of prescription testosterone. Can a doctor prescribe clomiphene for a man? Yes. It’s “off label”, meaning that it’s not FDA approved for use in men.
As a medication, clomiphene is usually well tolerated by men. In my experience, most patients don’t feel anything as their testosterone rises. Those that do feel an increase in energy, sex drive, and muscle mass, especially if they work out. Very rarely I’ve had patients report that they feel too aggressive, or too angry. Very very rarely (twice in the last 20 years) I’ve had patients report visual changes. That’s worrisome, as the pituitary is near the optic nerve in the brain, and visual changes suggests that the pituitary may be changing in size. Because the skull is a closed space, it’s alarming if anything in the brain changes in size. In the last twenty years, I’ve also had two patients who had breast enlargement (called “gynecomastia”) while using clomiphene. Needless to say, for any of these problematic side effects, the clomiphene is discontinued.
So that’s the story with clomiphene. It can be used in the male, either for fertility or low testosterone levels. It’s an off label prescription drug. It works, and is usually well tolerated by men who take it.